The Myriapoda of Halimun-Salak National Park (Java, Indonesia)
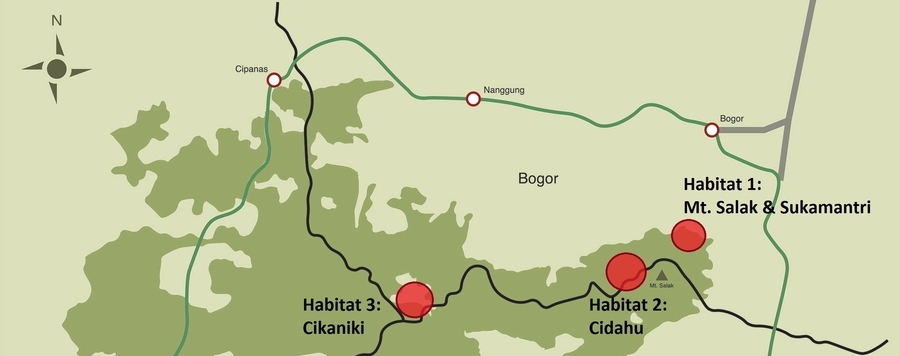
The myriapod fauna of the mega-diverse country of Indonesia is so far insufficiently known, with no species lists or determination keys. In order to obtain an overview of the faunal composition of the Myriapoda in an Indonesian forest system, the fauna of the Halimun-Salak National Park in western Java was explored during the dry season (September–October 2015) in the framework of the German-Indonesian INDOBIOSYS project (Indonesian Biodiversity Discovery and Information System). A total of 980 Myriapoda specimens were collected by hand by 3–4 researchers from three different sites in the national park, from which 796 specimens were determined to a higher taxonomic level (class, order, family) and 617 specimens were determined to morphospecies. Among these, 27 were Symphyla (4%) (excluded from further analyses), 226 Chilopoda (28%) and 543 Diplopoda (68%). The Scolopendromorpha (64% of all identified centipedes) and Polydesmida (69% of all identified Diplopoda) were the most represented orders in our samples. Twenty-four morphospecies of Chilopoda were determined: one each of Scutigeromorpha and Lithobiomorpha, six Scolopendromorpha and sixteen Geophilomorpha. Nine orders of diplopods were present, with a total of 47 morphospecies: one each of Polyxenida, Glomeridesmida and Chordeumatida, two each of Glomerida, Spirobolida and Siphonophorida, seven of Sphaerotheriida, ten of Spirostreptida and 21 of Polydesmida. Two species curves were obtained to have a first idea about the myriapod diversity in the Halimun-Salak National Park and to compare the three individual collecting sites. Our results depict the Scolopendromorpha as the most common centipedes in Javanese rainforests and the Geophilomorpha as the most species-rich order. In contrast, the Polydesmida were the most dominant millipede group with 167 specimens and with 13 morphospecies the family Paradoxosomatidae was the most diverse.






