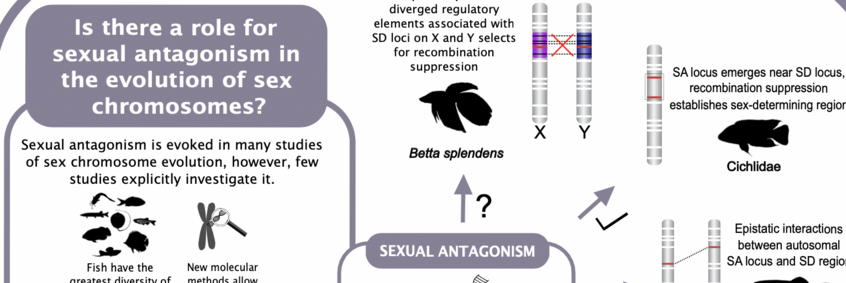
Sexual antagonism in the evolution of sex chromosomes
The recent increase in available molecular and genomic data for diverse taxa helps to shed new light on long-standing theories. Research into sex chromosome evolution has particularly benefited from a growing number of studies of fish, motivated by their highly diverse mechanisms of sex determination. Sexual antagonism is regularly cited as an influential force in sex chromosome emergence; however, this so far proves difficult to demonstrate. In this review, we highlight recent developments in the investigation of sexual antagonism in sex chromosome research in fish. We find strong emphasis placed on study-organism specific genomic features and patterns of recombination, rather than evidence for a comprehensive role of sexual antagonism. In this light, we discuss the alternative models of sex chromosome evolution. We conclude that fish represents a key resource for further research, provided attention is given to species-specific effects while simultaneously integrating comparative studies across taxa for a vital and comprehensive understanding of sex chromosome evolution and investigation of proposed models.





