Scale Morphology and Micro-Structure of Monitor Lizards
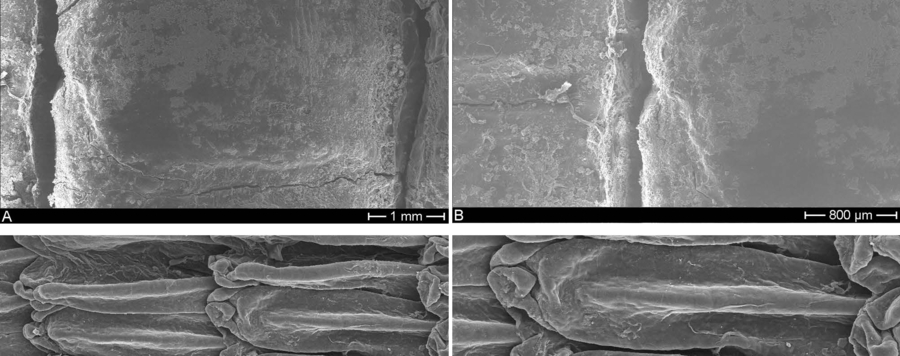
We analysed scale morphology and micro-structure from five different body regions using scanning electron microscopy (SEM) across all nine recognized subgenera of the monitor lizard genus Varanus including 41 different species investigated. As far as we are aware, this qualitative visual technique was applied by us for the first time to most monitor lizard species and probably also to the primary outgroup and sister species Lanthanotus borneensis. A comprehensive list of 20 scalation characters each with up to seven corresponding character states was established and defined for the five body regions sampled. For the phylogenetic approach, parsimony analyses of the resulting morphological data matrix as well as Bremer and bootstrap support calculations were performed with the software TNT. Our results demonstrate that a variety of micro-ornamentations (i.e., ultra- or micro-dermatoglyphics) as seen in various squamate groups is hardly present in monitor lizards. In several species from six out of nine subgenera, however, we found a honeycomb-shaped micro-structure of foveate polygons. Two further samples of Euprepiosaurus Fitzinger, 1843 exhibit each another unique microscopic structure on the scale surface. Notably, the majority of species showing the honeycombed ultra-structure inhabit arid habitats in Australia, Africa and the Middle East. Therefore, it can be inferred that this microscopic scalation feature, which has also been identified in other desert dwelling lizard species, is taxonomically and ecologically correlated with a xeric habitat type in varanids, too. In addition, the systematic affiliation of V. spinulosus, an endemic monitor lizard species from the Solomon Islands with an extraordinary scale shape, is discussed in the light of current hypotheses about its phylogenetic position within the Varanidae. Due to its unique scalation characteristics, in combination with other morphological evidence, a new monotypic subgenus, Solomonsaurus subgen. nov., is erected for this enigmatic monitor lizard species. Furthermore, we propose a taxonomic splitting of the morphologically and ecologically heterogeneous subgenus Euprepiosaurus comprising the Pacific or mangrove and the tree monitor lizards, respectively, again based on the SEM data. Thus, for the members of the highly arboreal V. prasinus species group erection of a new subgenus, Hapturosaurus subgen. nov., is justified based on the autapomorphic scale shape in concert with further morphological, phylogenetic and ecological evidence. In addition, V. reisingeri originally described as a distinct species is considered conspecific with the wide-spread V. prasinus due to joint synapormorphic features in the ventral scale micro-structure. Consequently, V. prasinus is (again) rendered polytypic with the taxon reisingeri being assigned subspecies status here. In conclusion, the established scalation characters allow discrimination of single species even among closely-related Varanus species, such as the members of the V. indicus species group. Together with a recently published identification key for Southeast Asian monitor lizards based on macroscopic phenotypic characters (Koch et al. 2013), the SEM-pictures of the present study may serve as additional references for the microscopic identification of CITES-relevant monitor lizard skins and products, respectively.






